|
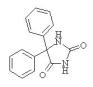
Phenytoin
(Diphenylhydantoin)
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Diphenylhydantoin (Dilantin)
Phenytoin
(
FEN-ih-toyn, dye-
fen-ill-hy-
DAN-toyn)
Pregnancy Category: C
Dilantin Infatab
Dilantin-125
Novo-Phenytoin
 Tremytoine
Tremytoine
 (Rx)
(Rx)
Phenytoin sodium, extended
Phenytoin sodium, extended (Dilantin Kapseals)
Phenytoin sodium
(
FEN-ih-toyn)
Pregnancy Category: C
Dilantin Kapseals
(Rx)
Phenytoin sodium, parenteral
Phenytoin sodium, parenteral (Dilantin Sodium)
Phenytoin sodium
(
FEN-ih-toyn)
Pregnancy Category: C
Dilantin Sodium
(Rx)
Phenytoin sodium prompt
Phenytoin sodium prompt (Diphenylan Sodium)
Phenytoin sodium
(
FEN-ih-toyn)
Pregnancy Category: C
Diphenylan Sodium
(Rx)
Classification:
Anticonvulsant, hydantoin type; antiarrhythmic (type I)
See Also:
See also
Anticonvulsants
[ and
Antiarrhythmic Agents
][.
]
Action/Kinetics:
Acts in the motor cortex of the brain to reduce the spread of electrical discharges from the rapidly firing epileptic foci in this area. This is accomplished by stabilizing hyperexcitable cells possibly by affecting sodium efflux. Also, phenytoin decreases activity of centers in the brain stem responsible for the tonic phase of grand mal seizures. Has few sedative effects.
Monitor serum levels because the serum concentrations of phenytoin increase disproportionately as the dosage is increased. Phenytoin extended is designed for once-a-day dosage. It has a slow dissolution rate--no more than 35% in 30 min, 30%-70% in 60 min, and less than 85% in 120 min. Absorption is variable following PO dosage.
Peak serum levels: PO, 4-8 hr. Since the rate and extent of absorption depend on the particular preparation, the same product should be used for a particular client.
Peak serum levels (following IM): 24 hr (wide variation).
Therapeutic serum levels: 5-20 mcg/mL.
t
1/2: 8-60 hr (average: 20-30 hr).
Steady state: 7-10 days after initiation. Biotransformed in the liver. Both inactive metabolites and unchanged drug are excreted in the urine.
As an antiarrhythmic, phenytoin increases the electrical stimulation threshold of heart muscle, although it is less effective than quinidine, procainamide, or lidocaine.
Onset: 30-60 min.
Duration: 24 hr or more.
t
1/2: 22-36 hr.
Therapeutic serum level: 10-20 mcg/mL.
Uses:
Chronic epilepsy, especially of the tonic-clonic, psychomotor type. Not effective against absence seizures and may even increase the frequency of seizures in this disorder. Parenteral phenytoin is sometimes used to treat status epilepticus and to control seizures during neurosurgery.
PO for certain PVCs and IV for PVCs and tachycardia. Particularly useful for arrhythmias produced by digitalis
overdosage.
Investigational: Paroxysmal choreoathetosis; to treat blistering and erosions in clients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; episodic dyscontrol; trigeminal neuralgia; as a muscle relaxant in neuromyotonia, myotonia congenita, or myotonic muscular dystrophy; to treat cardiac symptoms in overdosage of tricyclic antidepressants. Severe preeclampsia.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to hydantoins, exfoliative dermatitis, sinus bradycardia, second- and third-degree AV block, clients with Adams-Stokes syndrome, SA block. Lactation.
Special Concerns:
Use with caution in acute, intermittent porphyria. Administer with extreme caution to clients with a history of asthma or other allergies, impaired renal or hepatic function, and heart disease (hypotension, severe myocardial insufficiency). Abrupt withdrawal may cause status epilepticus. Combined drug therapy is required if petit mal seizures are also present.
Side Effects:
CNS: Most commonly, drowsiness, ataxia, dysarthria, confusion, insomnia, nervousness, irritability, depression, tremor, numbness, headache, psychoses,
increased seizures. Choreoathetosis following IV use.
GI: Gingival hyperplasia, N&V;, either diarrhea or constipation.
Dermatologic: Various dermatoses including a measles-like rash (common), scarlatiniform, maculopapular, and urticarial rashes. Rarely, drug-induced lupus erythematosus,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome exfoliative or purpuric dermatitis, and
toxic epidermal necrolysis. Alopecia, hirsutism. Skin reactions may necessitate withdrawal of therapy.
Hematopoietic: Leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia,
agranulocytosis macrocytosis, megaloblastic anemia, leukocytosis, monocytosis, eosinophilia, simple anemia,
aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia.
Hepatic: Liver damage, toxic hepatitis, hypersensitivity reactions involving the liver including hepatocellular degeneration and
fatal hepatocellular necrosis.
Ophthalmic: Diplopia, nystagmus, conjunctivitis.
Miscellaneous: Hyperglycemia, chest pain, edema, fever, photophobia, weight gain,
pulmonary fibrosis lymph node hyperplasia, gynecomastia, periarteritis nodosa, depression of IgA, soft tissue injury at injection site, coarsening of facial features, Peyronie's disease, enlarged lips.
Rapid parenteral administration may cause serious CV effects, including hypotension, arrhythmias, CV collapse, and heart block, as well as CNS depression.
Many clients have a partial deficiency in the ability of the liver to degrade phenytoin, and as a result, toxicity may develop after a small PO dose. Liver and kidney function tests and hematopoietic studies are indicated prior to and periodically during drug therapy.
Laboratory Test Alterations:
Alters LFTs,
 blood glucose values, and blood glucose values, and
 PBI values. PBI values.
 Gamma globulins. Phenytoin Gamma globulins. Phenytoin
 immunoglobulins A and G. False + Coombs' test. immunoglobulins A and G. False + Coombs' test.
Overdose Management:
Symptoms: Initially, ataxia, dysarthria, and nystagmus followed by unresponsive pupils, hypotension, and
coma. Plasma levels greater than 40 mcg/mL result in significant decreases in mental capacity.
Treatment: Treat symptoms. Hemodialysis may be effective. In children, total-exchange transfusion has been used.
Drug Interactions:
-
Acetaminophen /
 Acetaminophen effect R/T Acetaminophen effect R/T
 liver breakdown; hepatotoxicity may liver breakdown; hepatotoxicity may

-
Alcohol, ethyl /
 Phenytoin effect in alcoholics R/T Phenytoin effect in alcoholics R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Allopurinol /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Amiodarone /
 Phenytoin or amiodarone effect R/T Phenytoin or amiodarone effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Antacids /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 GI absorption GI absorption
-
Anticoagulants, oral /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown. Also, possible liver breakdown. Also, possible
 anticoagulant effect R/T anticoagulant effect R/T
 plasma protein binding plasma protein binding
-
Antidepressants, tricyclic /
 Risk of epileptic seizures or Risk of epileptic seizures or
 phenytoin effect by phenytoin effect by
 plasma protein binding plasma protein binding
-
Barbiturates / Phenytoin effect may be
 , ,
 , or not changed; possible , or not changed; possible
 effect of barbiturates effect of barbiturates
-
Benzodiazepines /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Carbamazepine /
 Phenytoin or cabamazepine effect R/T Phenytoin or cabamazepine effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Charcoal /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 absorption from GI tract absorption from GI tract
-
Chloramphenicol /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Chlorpheniramine /
 Phenytoin effect Phenytoin effect
-
Cimetidine /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Clonazepam /
 Plasma levels of clonazepam or phenytoin; Plasma levels of clonazepam or phenytoin;
 risk of phenytoin toxicity risk of phenytoin toxicity
-
Contraceptives, oral / Estrogen-induced fluid retention may precipitate seizures; also,
 effect of contraceptives R/T effect of contraceptives R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Corticosteroids /
 Corticosteroid effect R/T Corticosteroid effect R/T
 liver breakdown; also, corticosteroids may mask hypersensitivity reactions due to phenytoin liver breakdown; also, corticosteroids may mask hypersensitivity reactions due to phenytoin
-
Cyclosporine /
 Cyclosporine effect R/T Cyclosporine effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Diazoxide /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Dicumarol /
 Dicumarol effect R/T Dicumarol effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Digitalis glycosides /
 Digitalis effect R/T Digitalis effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Disopyramide /
 Disopyramide effect R/T Disopyramide effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Disulfiram /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Dopamine / IV phenytoin
hypotension and bradycardia; also,
 dopamine effect dopamine effect
-
Doxycycline /
 Doxycycline effect R/T Doxycycline effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Estrogens / See
Contraceptives, oral
-
Fluconazole /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Folic acid /
 Phenytoin effect Phenytoin effect
-
Furosemide /
 Furosemide effect R/T Furosemide effect R/T
 absorption absorption
-
Haloperidol /
 Haloperidol effect R/T Haloperidol effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Ibuprofen /
 Phenytoin effect Phenytoin effect
-
Isoniazid /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Levodopa /
 Levodopa effect Levodopa effect
-
Levonorgestrel /
 Levonorgestrel effect Levonorgestrel effect
-
Lithium /
 Risk of lithium toxicity Risk of lithium toxicity
-
Loxapine /
 Phenytoin effect Phenytoin effect
-
Mebendazole /
 Mebendazole effect Mebendazole effect
-
Meperidine /
 Meperidine effect R/T Meperidine effect R/T
 liver breakdown; toxic effects of meperidine may liver breakdown; toxic effects of meperidine may
 due to accumulation of active metabolite (normeperidine) due to accumulation of active metabolite (normeperidine)
-
Methadone /
 Methadone effect R/T Methadone effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Metronidazole /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Metyrapone /
 Metyrapone effect R/T Metyrapone effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Mexiletine /
 Mexiletine effect R/T Mexiletine effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Miconazole /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Milk thistle/ Helps prevent liver damage from phenytoin
-
Nitrofurantoin /
 Phenytoin effect Phenytoin effect
-
Omeprazole /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Phenothiazines /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Primidone / Possible
 primidone effect primidone effect
-
Pyridoxine /
 Phenytoin effect Phenytoin effect
-
Quinidine /
 Quinidine effect R/T Quinidine effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Rifampin /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Salicylates /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 plasma protein binding plasma protein binding
-
Sucralfate /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 absorption from GI tract absorption from GI tract
-
Sulfonamides /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Sulfonylureas /
 Sulfonylurea effect Sulfonylurea effect
-
Theophylline /
 Effect of both drugs R/T Effect of both drugs R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Trimethoprim /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
-
Valproic acid /
 Phenytoin effect R/T Phenytoin effect R/T
 liver breakdown and liver breakdown and
 plasma protein binding; phenytoin may also plasma protein binding; phenytoin may also
 effect of valproic acid R/T effect of valproic acid R/T
 liver breakdown liver breakdown
How Supplied:
Phenytoin:
Chew Tablet: 50 mg;
Suspension: 100 mg/4 mL, 125 mg/5 mL;
Phenytoin sodium, extended:
Capsule, Extended Release: 30 mg, 100 mg;
Phenytoin sodium, parenteral:
Injection: 50 mg/mL;
Phenytoin sodium prompt:
Capsule: 100 mg
Dosage
?Oral Suspension, Chewable Tablets
Seizures.
Adults, initial: 100 mg (125 mg of the suspension) t.i.d.; adjust dosage at 7- to 10-day intervals until seizures are controlled;
usual, maintenance: 300-400 mg/day, although 600 mg/day (625 mg of the suspension) may be required in some.
Pediatric, initial: 5 mg/kg/day in two to three divided doses;
maintenance, 4-8 mg/kg (up to maximum of 300 mg/day). Children over 6 years may require up to 300 mg/day.
Geriatric: 3 mg/kg initially in divided doses;
then, adjust dosage according to serum levels and response. Once dosage level has been established, the extended capsules may be used for once-a-day dosage.
?Capsules, Extended-Release Capsules
Seizures.
Adults, initial: 100 mg t.i.d.; adjust dose at 7- to 10-day intervals until control is achieved. An initial loading dose of 12-15 mg/kg divided into two to three doses over 6 hr followed by 100 mg t.i.d. on subsequent days may be preferred if seizures are frequent.
Pediatric: See dose for Oral Suspension and Chewable Tablets.
Arrhythmias.
Adults: 200-400 mg/day.
?IV
Status epilepticus.
Adults, loading dose: 10-15 mg/kg at a rate not to exceed 50 mg/min;
then, 100 mg PO or IV q 6-8 hr.
Pediatric, loading dose: 15-20 mg/kg in divided doses of 5-10 mg/kg given at a rate of 1-3 mg/kg/min.
Arrhythmias.
Adults: 100 mg q 5 min up to maximum of 1 g.
?IM
Dose should be 50% greater than the PO dose.
Neurosurgery.
100-200 mg q 4 hr during and after surgery (during first 24 hr, administer no more than 1,000 mg; after first day, give maintenance dosage). |







spel boy, rochester,ny - 03/30/2012
i hope they make a dilantin test for home use so your not so screwed,blued,and tatooed
replica watches Juppy, replica watches Juppy - 08/20/2012
zenith replica watches <a href="http://bigreplicastore.com/">swiss replica watches movado</a> replica watches longines http://bigreplicastore.com/ - replica quartz watches replica watches jewelry iwc cartier omega
blethymutty, blethymutty - 12/15/2012
Happens... Such casual concurrence <a href="http://bestgenericviagra.biz/#2993">generic viagra</a> http://bestgenericviagra.biz/ viagra prices walgreens , <a href="http://bestgenericcialis.com/#3332">cheap generic cialis</a>. cialis professional 10 mg .
lulpthfd, lulpthfd - 03/29/2013
lulpthfd
muvbvwp http://gkklxg.com/ <a href="http://chpgzm.com/ ">qkwfwoit</a> [url=http://ebdvpg.com/]qkwfwoit[/url], muvbvwp http://gkklxg.com/ <a href="http://chpgzm.com/ ">qkwfwoit</a> [url=http://ebdvpg.com/]qkwfwoit[/url] - 03/30/2013
muvbvwp http://gkklxg.com/ <a href="http://chpgzm.com/ ">qkwfwoit</a> [url=http://ebdvpg.com/]qkwfwoit[/url]